CT Angiography
What is Coronary CT Angiography?
Coronary CT Angiography (CTA) is a non-invasive imaging test that uses computed tomography technology to produce high-resolution images of the heart and its blood vessels. It is a valuable tool in cardiology because it can detect blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle. There are several advantages to CTA over other traditional cardiac testing modalities.
-
Because coronary CT angiography is a non-invasive procedure, it does not require any incisions or catheters to be inserted into the body.
-
The test is quick and efficient, taking less than an hour to complete, which means less disruption to your busy schedule.
-
Coronary CT angiography has a high accuracy rate for detecting blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries, with a sensitivity and specificity of over 95%.
-
Recent advancements in technology have significantly reduced the amount of radiation exposure during the test, making it safer for patients.
The Role of Coronary CT Angiography
Diagnosing coronary artery disease: Coronary CT angiography is an effective tool for diagnosing coronary artery disease. It can detect even small blockages in the coronary arteries, which may be missed by other diagnostic tests.
Planning Treatment: Coronary CT angiography can help cardiologists determine the best treatment plan for patients with coronary artery disease, including medication, lifestyle changes, or invasive procedures like angioplasty and stenting or bypass surgery.
Monitoring Progression of Coronary Artery Disease: Coronary CT angiography can also be used to monitor the progression of coronary artery disease over time, and to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments.
Identifying Other Conditions: In addition to coronary artery disease, coronary CT angiography can also detect other conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels, such as aneurysms, dissections, or pulmonary embolism.
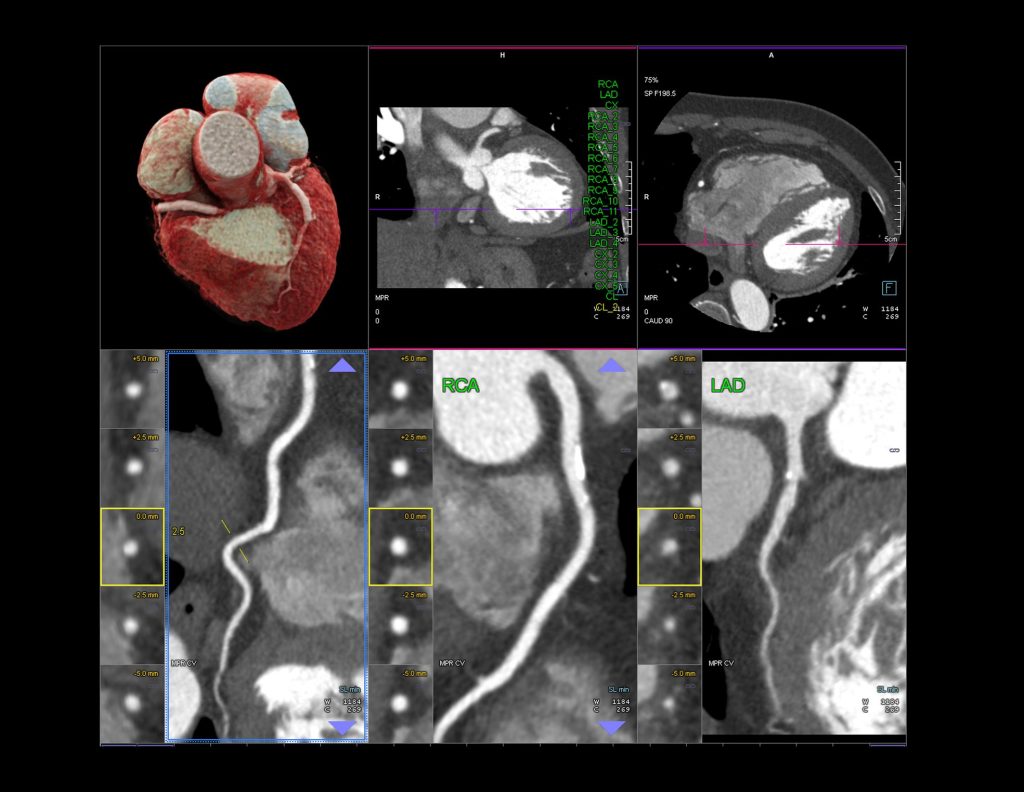
Additional Applications: FFRCT
FFRCT (fractional flow reserve computed tomography) is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides valuable information about blood flow in the coronary arteries. FFRCT analysis combines anatomic and physiologic information in a single non-invasive cardiac test that provides clinicians with higher diagnostic performance and accuracy than other non-invasive tests. It uses computed tomography (CT) technology to measure the pressure and flow of blood through narrowings or blockages in the coronary arteries.
FFRCT is a simulation of invasive FFR, a diagnostic test that involves measuring blood pressure and flow in the coronary arteries using a catheter. FFRCT, on the other hand, is a non-invasive test that uses advanced computer algorithms to analyze CT images of the heart and generate a simulated FFR value. FFRCT provides highly accurate information about blood flow in the coronary arteries, which can help cardiologists make more informed decisions about treatment options. With the aid of this new technology, cardiologists can determine which patients can benefit from invasive assessment while avoiding invasive procedures for patients without blood-flow limiting coronary artery disease.
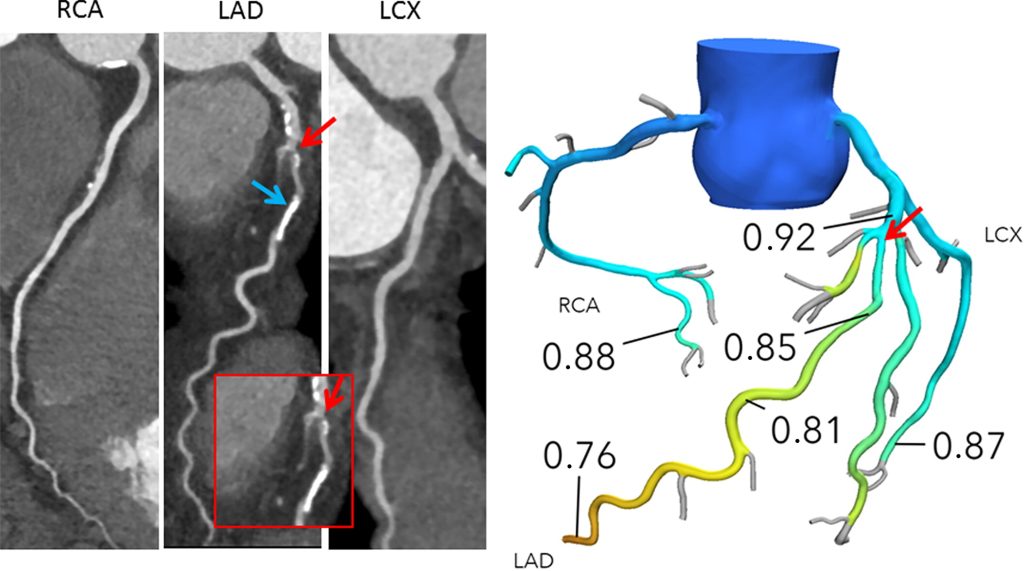
The newly updated American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Guidelines reflect the growing support for a Coronary CTA + FFRCT pathway across the world – including in Europe, the United Kingdom, and Japan – suggesting a revolutionary shift in the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease is underway.